What is Amortization: Definition, Formula, Examples

Each payment decreases the asset’s value on the balance sheet, displaying its loss in value over time. The business records the expense on the income statement, reducing the company’s net income. It is the gradual principal amount repayment along with amortization definition accounting interest through equal periodic payments. As a result, the outstanding loan or debt balance keeps reducing over time until it turns to zero. First, amortization is used in the process of paying off debt through regular principal and interest payments over time.

Amortization of Loans
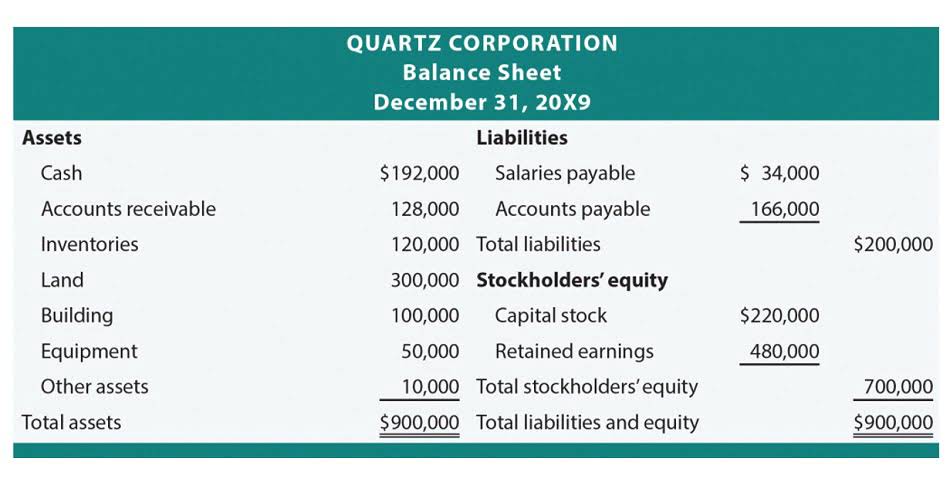
The historical cost of HVAC Bookkeeping fixed assets remains on a company’s books; however, the company also reports this contra asset amount as a net reduced book value amount. Amortization is a certain technique used in accounting to reduce the book value of money owed, like a loan for example. It can also get used to lower the book value of intangible assets over a period of time.
- With every passing month, as the principal balance drops, so does the amount of new interest accruing, gradually making room for more of your payment to diminish the principal.
- The journal entry for interest accrued on a borrowed sum includes debiting the Interest Expense account and crediting the Accrued Interest Payable account.
- In such cases, you may find amortization is a beneficial accounting method.
- With a short expected duration, such as days or months, it is probably best and most efficient to expense the cost through the income statement and not count the item as an asset at all.
- In general, the word amortization means to systematically reduce a balance over time.
What Is a 30-Year Amortization Schedule?
- This method is usually used when a business plans to recognize an expense early on to lower profitability and, in turn, defer taxes.
- Understanding fully amortizing payments is essential for managing loans, mortgages, or long-term financial obligations.
- Taking these insights on accrued interest to heart, it’s time to turn theory into action.
- Each subsequent payment is a greater percentage of the payment goes towards the loan’s principal.
- Another common circumstance is when the asset is utilized faster in the initial years of its useful life.
- For example, in the first month, about $1,000 of the $1,432.25 would cover interest, while $432.25 reduces the principal.
- Dreamzone divided the purchase price by the useful life to amortize the patent’s cost.
It is also useful for planning to understand what a company’s future debt balance will be after a series of payments have already been made. The loan term and interest rate play a critical role in determining fully amortizing payments. The loan term, or repayment duration, influences the size of monthly payments.

Advance Your Accounting and Bookkeeping Career
It’s a technique used to help reduce the book value of any loans you have. When it comes to handling loans, you would use amortization to help spread out the debt principal over a period of time. It’s the process of paying off those debts through pre-determined and scheduled installments. Let’s say, it’s the 25-year loan you can take, but you should fix your 20-year loan payments (assuming your mortgage allows you to make prepayments). You could just change your monthly payments without a penalty for 25 years if you are ever faced with financial difficulties. The purchase of a house, or property, is one of the largest financial investments for many people and businesses.

- With this, we move on to the next section which clears out if amortization can be considered as an asset on the balance sheet.
- Consequently, the company reports an amortization for the software with $3,333 as an amortization expense.
- In a loan amortization schedule, this information can be helpful in numerous ways.
- The amortization period refers to the duration of a mortgage payment by the borrower in years.
- You could just change your monthly payments without a penalty for 25 years if you are ever faced with financial difficulties.
With every passing month, as the principal balance drops, so does the amount of new interest accruing, gradually making room for more of your payment to diminish the principal. So, think of regular interest as a fixed photo on your financial mantelpiece, while accrued interest is more like a slideshow, constantly updating until the moment you freeze it into a payment. By grasping both concepts, you can better manage your loans, savings, and investments to ensure no surprises when it comes to the actual costs or earnings in your financial adventures. Now, whether you’re dealing with a savings account, a bond, or a loan, the principle remains the same, but the timing can change things. With some loans, that interest might pile up daily, making a slightly bigger snowball each day.
Browse Glossary Term
For companies, it helps in accurately representing the declining value of intangible assets, ensuring the financial statements provide a true reflection of the company’s economic position. For individuals, especially those with loans, comprehending the concept of amortization can aid in informed decision-making and planning regarding their financial obligations. Amortization is a financial concept that retained earnings allows an asset or a long-term liability cost’s gradual allocation or repayment over a specific period. This method helps in matching the expenses with the revenue or benefits generated by an asset or liability over time with accuracy. Furthermore, amortization in accounting offers a more accurate representation of a company’s financial performance.
